What Is Qubits In Quantum Computing
Category: QUANTUM COMPUTING | 18th December 2023, Monday
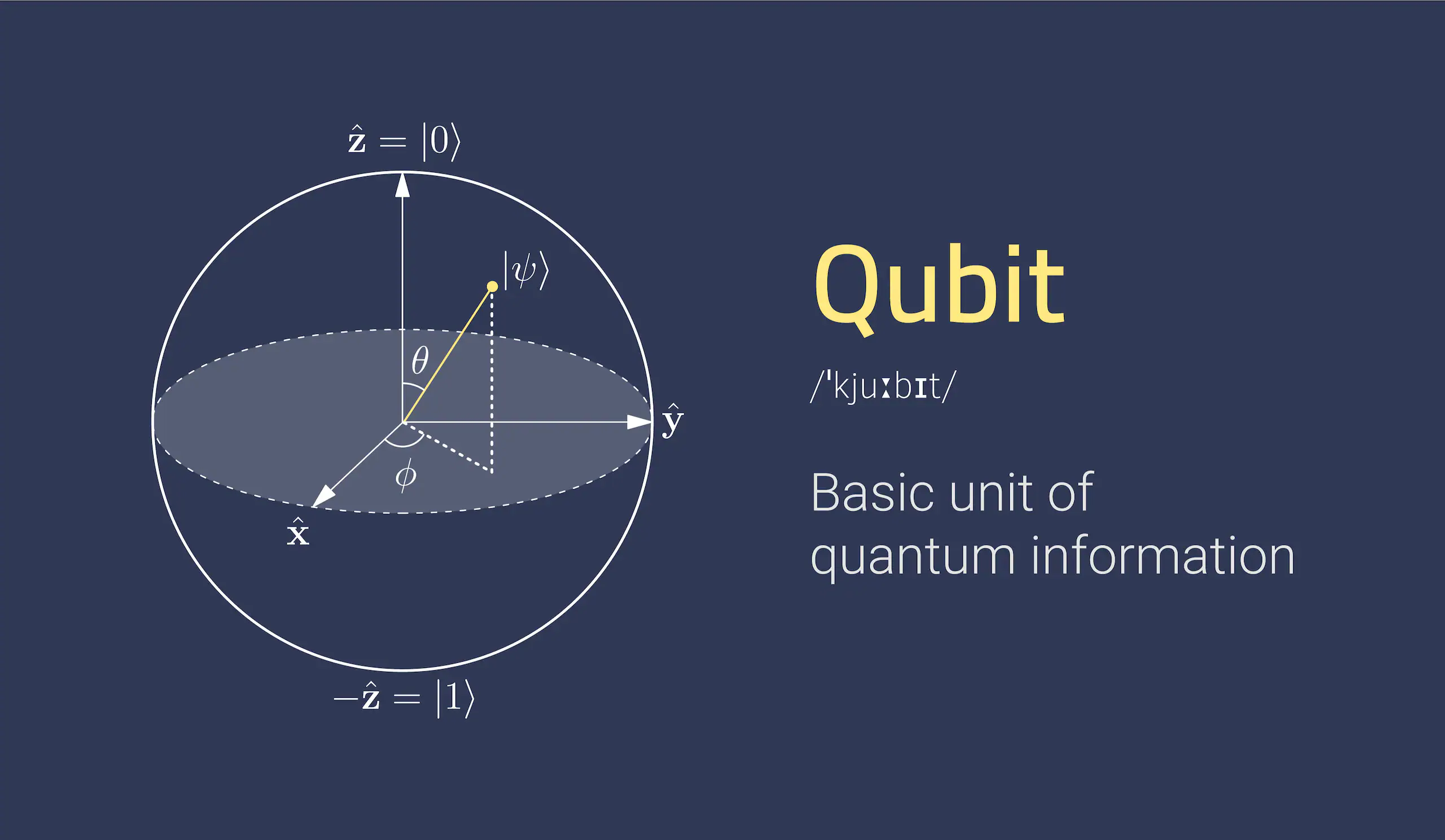
In Quantum Computing, A Qubit, Short For "quantum Bit," Is The Fundamental Unit Of Quantum Information. Unlike Classical Bits In Classical Computing, Which Can Exist In One Of Two States (0 Or 1), Qubits Can Exist In Multiple States Simultaneously Due To The Principles Of Quantum Superposition.
The Key Features Of Qubits Are:
-
Superposition: A Qubit Can Exist In A Superposition Of States, Representing Both 0 And 1 Simultaneously. This Enables Quantum Computers To Perform Parallel Computations On A Large Scale.
-
Entanglement: Qubits Can Be Entangled, Meaning The State Of One Qubit Is Directly Related To The State Of Another, Regardless Of The Physical Distance Between Them. Changes To One Entangled Qubit Will Instantaneously Affect The Other, Providing A Powerful Mechanism For Quantum Information Processing.
-
Quantum Interference: Quantum Computers Leverage The Interference Of Probability Amplitudes To Enhance Correct Outcomes And Reduce The Likelihood Of Incorrect Ones During Computation.
These Quantum Properties Allow Quantum Computers To Solve Certain Problems Much More Efficiently Than Classical Computers. Quantum Computing Is Still In The Early Stages Of Development, And Practical, Large-scale Quantum Computers Are Yet To Be Realized. Researchers And Engineers Are Actively Working On Overcoming Various Challenges, Such As Maintaining Qubit Coherence And Reducing Error Rates, To Build More Robust And Scalable Quantum Computing Systems.
Tags:
Qubits, Qubit, Qubits In Quantum Computing
